A SOCKS5 proxy allows you to reroute the traffic from a specific client through a remote server before it reaches its destination. This spoofs your physical location and masks your true IP address from other websites and services you connect to on the internet.
SOCKS5 (Socket Secure 5) is the most recent version of SOCKS. Unlike its predecessors, it supports some forms of encryption and also offers authentication methods which ensure that only authorized users can access a given server.
SOCKS proxies can route data from a multitude of different sources including HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, and FTP – which makes them far more flexible than traditional HTTP or HTTPS proxies.
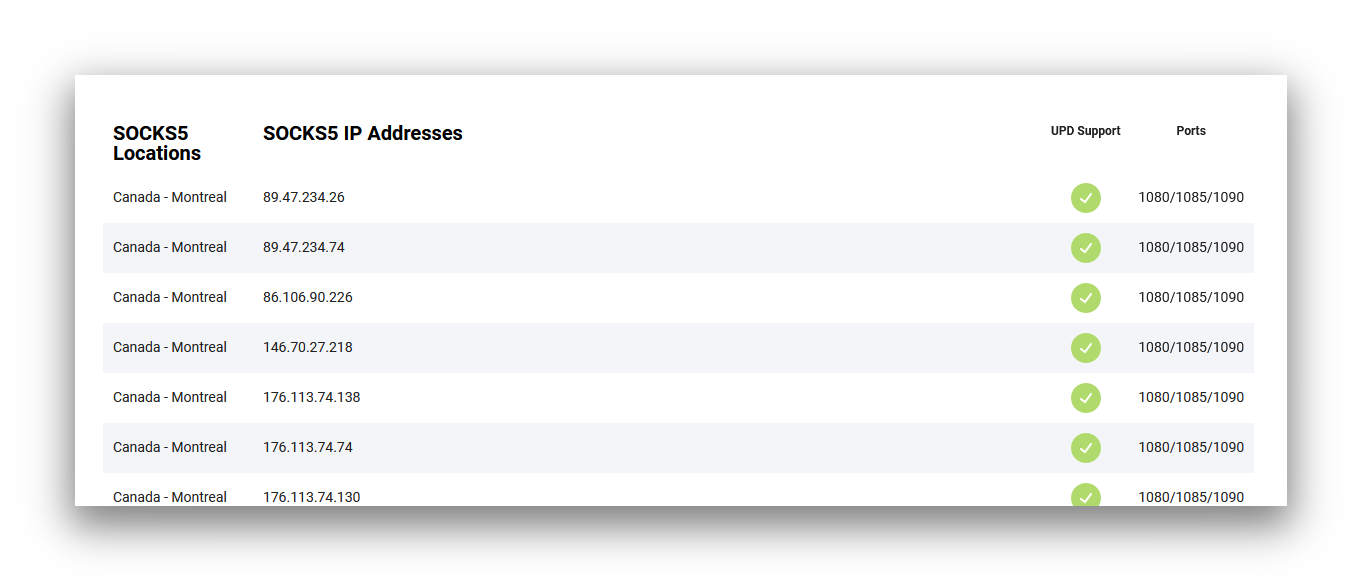
A small number of VPNs now provide SOCKS5 proxy servers as part of their service. This allows you to choose between a VPN server or a SOCKS5 proxy server.
While both SOCKS5 proxies and VPN services improve your online privacy, only a VPN will encrypt your traffic by default.
SOCKS5 proxies are often used for:
- Torrenting. Like VPNs, SOCKS5 proxies can mask your IP address. This is necessary for safe torrenting, as it helps protect you from copyright trolls and malicious third parties.
SOCKS5 proxies don’t always encrypt your traffic, which means they can download torrents much faster than VPN services. They are also less likely to conflict with peer-to-peer connections and seeding.
For this reason, many top torrenting VPNs offer access to SOCKS5 proxy servers.
- Bypassing censorship. SOCKS5 proxies use a TCP connection, which is less easily identifiable than most VPN protocols. Much like VPN obfuscation, this improves your chances of bypassing local censorship without being blocked by your ISP.
In fact, VPNs that work in China and other highly-censored countries often use a protocol called ShadowSOCKS, which mimics the kind of TCP connection used by SOCKS5 proxies.
- Remote network connection. If configured correctly, SOCKS5 proxies can permit remote access to a local network. They can make your device appear to be within that network in order to bypass the router’s firewall.
You can use this feature to access your home network remotely, or use it to access a company or university intranet. It’s more common to use a VPN for remote access, though, as it’s considered more secure.
How Does SOCKS5 Work?
SOCKS5 is an internet protocol that routes internet traffic via a remote server using a TCP connection. Before your traffic reaches its location, the server generates an arbitrary IP address to mask your actual IP address.
TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol. Alongside UDP (User Datagram Protocol) it is one of the two main protocols that allows computers to exchange information over a network. It is designed to ensure data integrity and prevent information loss.
In basic terms, SOCKS5 uses TCP to package your internet traffic and send it via a remote server before allowing it to reach the wider internet. The connection is typically unencrypted, though this depends on how the proxy is set up.
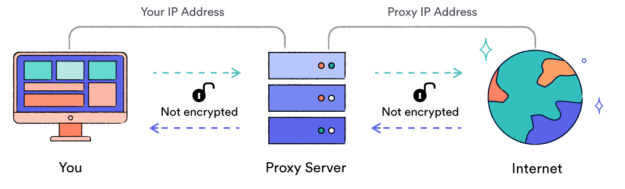
How a typical proxy server works to reroute your web traffic.
SOCKS5 operates on layer 5 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, above TCP and UDP. This means it can route anything operating on a lower level, which includes the vast majority of web applications including email, web browsing and P2P file-sharing.
Other proxies, like HTTP or HTTPS proxies, operate on a lower OSI layer. This means they can only route one kind of traffic, which is usually web browsing.
SOCKS5 differs from other SOCKS protocols by adding the option for authentication. There are three kinds of authentication available:
- Null authentication. This means there is no authentication, and anyone with the server IP address and port number can connect.
- Username/password. This requires users to input a correct password and username before connecting.
- GSS-API. The user and server both utilize authentication methods to verify each other before allowing a connection.
Is SOCKS5 Safe to Use?
SOCKS5 is a trusted and well-tested proxy protocol. It’s open-source, which means anyone can test it for insecurities, backdoors, or malicious alterations.
While SOCKS5 proxies are considered safe to use, they do present two key security weaknesses:
- The server provider could intercept your traffic
- SOCKS5 does not encrypt your traffic by default
Like a VPN, SOCKS5 proxies route your traffic through a third-party server. It’s important that you trust this third party, because they technically have the ability to monitor or manipulate your browsing data.
Unlike VPN services, though, SOCKS5 proxies do not encrypt your traffic. This means that while it may help you circumvent a firewall or other content blocks on your local network, your browsing activity may still be visible to your ISP, employer, or network administrator.
If you are using a SOCKS5 proxy to circumvent censorship, it could also allow your government to see what you are accessing.
If you’re using your proxy with a web browser, both of these issues are mitigated by HTTPS, which encrypts the data that’s sent between your browser and any HTTPS websites you visit.
This makes Man-in-the-Middle attacks harder, and means your ISP or network administrator will only be able to see the domains you visit, not the individual pages.
On balance, SOCKS5 proxies are safe to use, provided you use a trustworthy provider. In general, they do not offer the same level of security as a VPN, though. We recommend that you always use authentication, to minimize risk.